Introduction
Many times, when we buy a product, we also calculate our transportation costs so that we can finally find out how much it cost us to get that product, apart from the direct cost of the purchase. Now imagine that you have to pay for parking on the way to and from, in this case you will consider it as part of your cost. In all these cases, we seek to calculate the unit costs we have purchased. Now, if you did not leave the house with the sole intention of buying that specific item, and you do several things, one of which is the purchase of said item, you will only add a part of the parking fees to your purchased items and not all of them, and this concept Sharing is also mentioned in this simple example.
This small daily challenge for us, in businesses, mainly becomes a serious challenge; Because the organization has transitory direct and indirect products and costs, which must be correctly classified and distributed in the end, so that it shows itself in the calculation of the cost of goods sold (COGS) and the organization knows that in the end, the production (or provision) of a unit of goods with Considering all the related direct and indirect costs and as a result, can do the sales pricing correctly and competitively. In addition, it is necessary to identify the other costs of the organization correctly and show them in the company’s profit and loss statement.
Calculating the COGS in manufacturing companies is also much more difficult. Imagine a manufacturing company that works to produce a set of goods and provide it to the market. In order to calculate the unit cost for this company, in addition to the direct costs of manpower, machinery and raw materials that are directly involved in the production of products, it is necessary to correctly calculate the overhead costs and staff costs that are related to the manufactured goods. share and include in the calculation of the unit cost, costs such as the cost of restaurants, security or consumables such as paper and pens that are related to the production sector and for the production of goods must be included. Therefore, the multiplicity of costs and the commonality of some costs, along with the difficulty of dividing and separating the costs related to production, has made the calculation of the unit cost a serious challenge in many organizations.
Cost accounting and cost of goods sold
According to the above explanations, we will once again review the definition of unit cost: direct costs related to the production of goods sold in a company are called COGS (unit costs). Therefore, the unit cost is all the cost of the consumables used to produce the goods, as well as the direct costs of the production labor involved in the production of the respective goods. Costs such as distribution and sales, which are considered indirect costs, are not considered in the calculation of the COGS. However, indirect costs related to production must be considered.
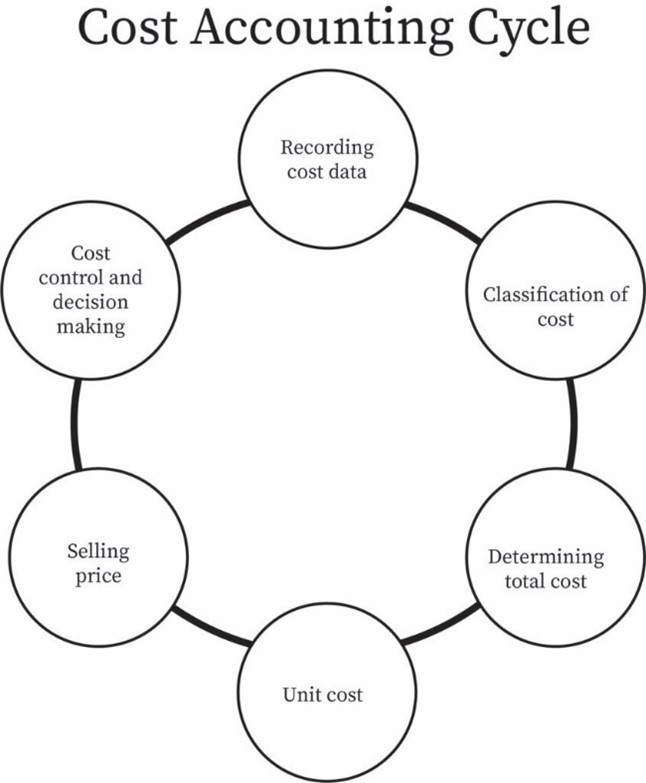
Due to the fact that the cost of goods sold (COGS) appears in the profit and loss statement and as a result is deducted from the organization’s revenues to calculate the company’s gross profit margin, the importance of cost accounting becomes a priority for organizations. Cost accounting is the name of a sub-branch of the accounting field in which things such as collecting information related to costs, calculating the cost of goods/services and examining methods of cost allocations are done. These activities are done by analyzing reports and examining production methods. There are different methods for calculating the unit costs, which are used based on the type and nature of the organization’s business and the goods. Among the most important methods used are:
- Average (moving weighted average)
- Standard
- FIFO
- LIFO
- Specific
Effective factors in calculating the unit cost
Generally, the effective factors and rules in calculating the unit cost are simple, and what makes the calculation of the unit cost difficult is not its rules, but its operation, reliable data, and finally the correct allocation of costs. The main components of calculating the cost of goods sold are:
- The cost of consumables (based on the consumption of materials and BOM)
- Direct wage cost (manpower direct production)
- Production overhead cost (costs such as indirect wages and depreciation and consumption of the line)
In other words, every cost that the organization makes to get the item manufactured (or commercial) goods to the warehouse in a salable condition should be included in this calculation. As you can see, the cost calculation rules are simple, but why is cost calculation a challenge for many organizations?
Performing the operations required to calculate the COGS is complex, and for this purpose the following two key elements are required in order to perform this operation correctly:
- Existence of accurate, structured and reliable data in the organization.
- The existence of a proper infrastructure to carry out the operations related to the classification and allocating of costs
The existence of the above factors, along with the knowledge of cost accounting and knowledge of different methods, can play an essential role in cost accounting.
Accurate, structured and reliable data
Cost data is the main input for costing operations. All costs must be structured, accurate and reliable and available centrally and without discrepancies. The existence of discrepancies and errors in the data, as well as the discreteness of the data in the different legacy systems and subsystems of the organization, and the challenge of collecting them is one of the problems of the organizations. Therefore, one of the important aspects of cost calculation is access to regular and accurate data of the organization in a suitable platform.
Appropriate infrastructure to carry out operations related to classification and cost allocation
If the required data is available, the organization needs a platform that can categorize its cost data, create cost centers related to its business and use them based on the parameters and formulas that meet the needs of the organization. Many organizations now perform these operations in general software such as Excel, which despite the power of Excel, the lack of specialization of the software and the high volume of manual operations and activities based on people’s tastes and methods, as well as files not being updated and numbers not being up-to-date, lead to the difficulty of operation and the lack of standardization of the process. Based on this, the organization needs a platform that can create its own cost structure in a standard way and share the costs based on standard principles and methods so that in addition to calculating the exact cost, other costs including administrative costs, sales and public expenses
should be properly calculated to be presented in financial statements.
Cost calculation software, Fiction or Reality?
If cost accounting software means a separate and ready-made software that by default predicts the rules and details of your business and quickly and automatically calculates the cost of goods/services, it is a sweet but unattainable dream. Is. Cost calculation and cost accounting in general are different in each organization; This is because the structure of costs and how to share them cannot be standardized for any two companies, and as a result, by having a separate software and manually entering information into it, the correct unit cost can be obtained as an output. Therefore, it can be said that the correct and accurate calculation of the unit cost in any organization requires the analysis and implementation of the correct informational and operational structure to achieve the desired result.
However, what is the solution and how can organizations give an appropriate answer to this issue of will? We will answer this question in the following.
How is the exact calculation of the unit cost achieved?
The reality of all businesses is the close and intertwined relationship of all the processes of the organization, including purchasing, selling, production, warehouse, financial accounting and cost accounting. The best infrastructure for calculating the unit cost should also be able to represent this intertwining and continuous communication of the organization’s processes and see the entire value chain of the organization in an integrated platform. Also, in terms of information structure, it is necessary to have a standard structure in the database and to support the standards in the field of financial-accounting and cost accounting and to have the necessary infrastructure for classification, categorization, division and allocation.
The most well-known platforms in the world with the above features are standard ERP solutions. The comprehensive enterprise resource planning solution or ERP includes a wide range of activities and processes, which leads to the improvement of the organization’s performance by organizing all the data and processes of the organization in a single solution and by creating a regular, continuous and accurate information database. Standard ERPs are data-oriented solutions and can solve the problem of correct and online data from all processes in the organization and become a reliable source for the organization. Note that ERP is initially a managerial concept, and then various tools have been developed by large software companies such as Microsoft on this concept.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software are systems that integrate data across the organization and provide it to the users who need it at the right time based on access levels. Such a system allows all the people of a group to work together in perfect harmony even if they are geographically dispersed.
Standard ERP solutions, in addition to centralizing the organization’s data in all main process areas, including purchasing, sales, finance, warehouse production, project, service management, as well as human resources, tools and infrastructure necessary to calculate the cost, categorize and It provides cost data classification and allocation. Also, due to the fact that ERP systems are not just ready to use softwares and require deployment and implementation services, therefore, the requirements of each set in the field of cost accounting are also taken into account and operationalized in the implementation phase to organize a reliable infrastructure, reliable from the point of view of data, as well as according to your real and specific needs of organizations.
Cost calculation in ERP Dynamics 365 Business Central Microsoft
First of all, due to its integrated nature, this ERP has financial-accounting, purchasing and procurement, sales and marketing, warehousing and inventory control, manufacturing and production, service management, project management and human resources modules, and all core processes of business and It covers the work of the organization. Therefore, all the data related to the key processes of the organization in this system are produced in a standard structure and there are details. Therefore, the organization will not be limited in accessing accurate data. On the other hand, ERP Dynamics 365 Business Central has standard and optimum processes (Best Practice) and in addition to the standard platform for the organization’s processes, it provides the infrastructure needed to calculate the unit cost. In the following, we will describe the main features and key elements of this system in the field of cost and industrial accounting:
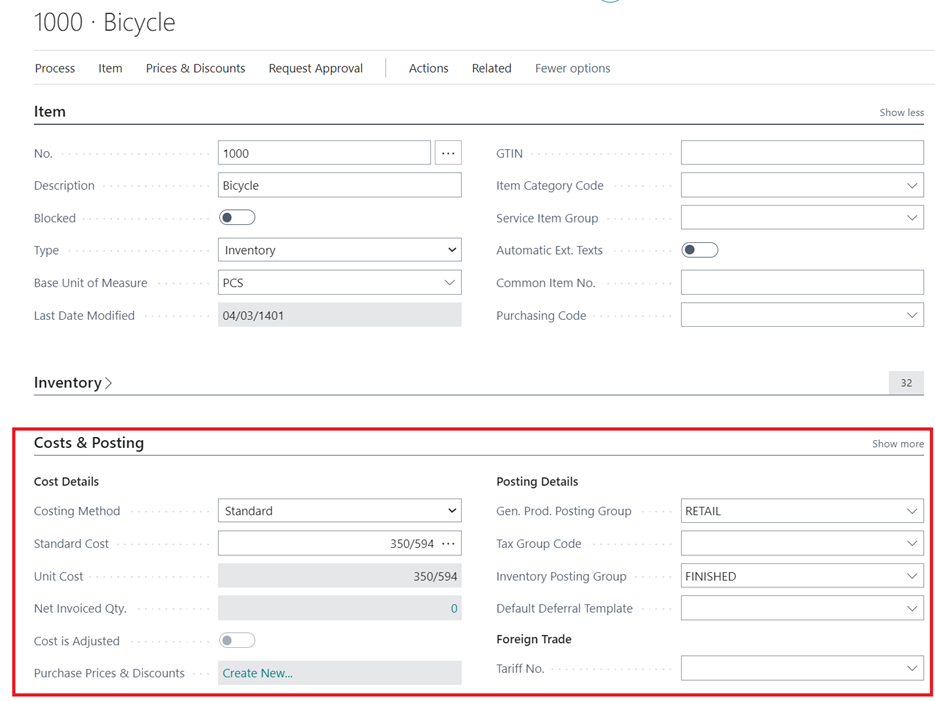
- The possibility of assigning different pricing methods to items in Business Central
We know that there are several methods for calculating the unit cost that are widely used in organizations, depending on the business and type of goods. In this system, it is possible to consider different methods for calculating the unit cost for different goods in the organization, including the average method, standard method, special identification, etc. In the image below, you can see an example of the item card and the methods that can be selected for its valuation.
- The full price of the purchased goods with the possibility of adding additional costs (Item Charge) for Purchasing goods and materials in Business Central
Let’s go back to the example at the beginning of this article, where the purchase side costs should be added to the direct purchase cost and this should be done correctly. In the process of purchasing and supplying raw materials for manufacturing companies or the final product in commercial companies, it is always necessary to identify and share the purchase costs correctly so that the unit cost of the purchased product is calculated correctly. Including costs such as transportation, insurance, customs, license and other overhead costs that are necessary to deliver the relevant goods to the organization’s warehouse, should be included. This possibility is considered in ERP Dynamics 365 Business Central as Item Charge, which can add additional costs to the purchase order and distribute them based on weight, dimensions, number, etc. on each item.
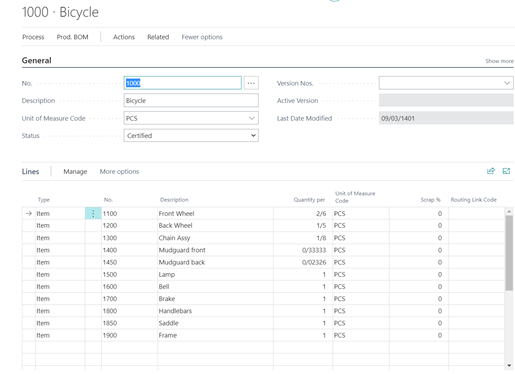
Quantity and cost of consumables by registering BOMs for manufactured and assembled items in Business Central
One of the components of calculating the cost of manufactured goods is the cost of consumables in production. In this system, every manufactured product can have a BOM (list of materials, list of consumption) to maintain both the required components and consumables and their consumption coefficient, and during the production of the corresponding product, the desired BOM can be called and after production, the relevant expenses should be recorded and included in the calculation of the cost of the manufactured goods. In the image below, you can see an example of the definition of a production BOM. It should be mentioned that BOM is also defined for assembled goods. Consumption can also be measured in different units.
- Cost of production operations for each activity by recording direct, indirect and overhead costs of each activity in the production line
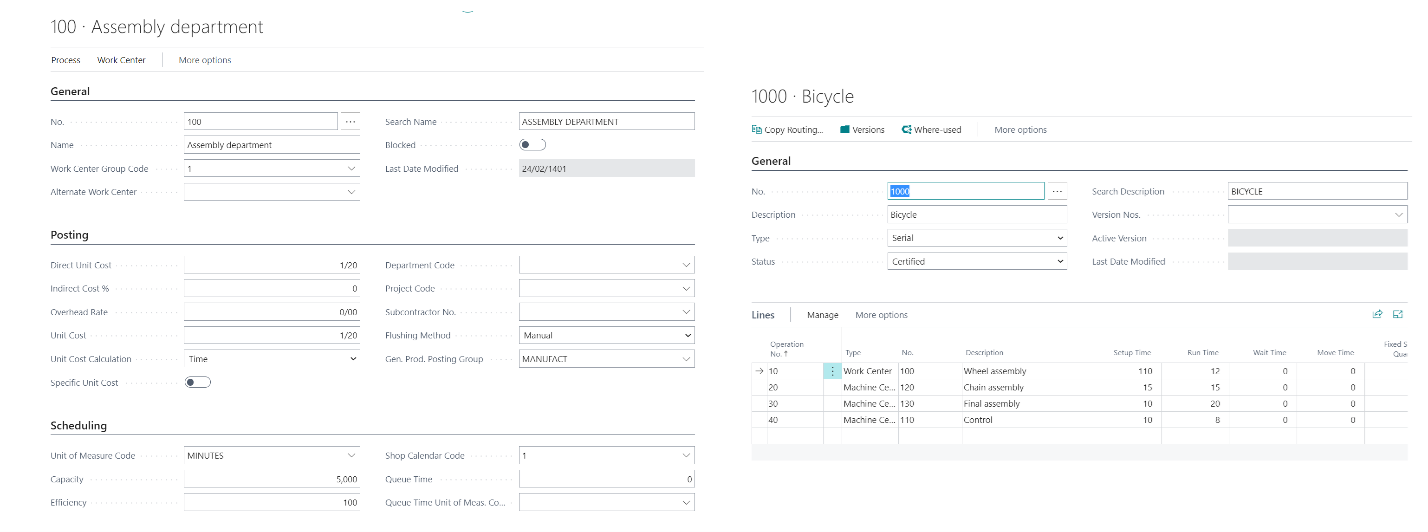
In ERP Dynamics 365 Business Central, you can define a work center (or machine center) for each step and each activity performed in the production line – whether this activity is related to production machines and devices or to production manpower and record the direct, indirect and overhead costs of that stage or production activity and also specify the production method of each product in defining the sequence of these workstations. In addition, define all the times related to the relevant operations, queue, transfer and preparation, so that finally it is determined what activity and to what extent each work center does on the manufactured product and how much it increases the finished price. In the image below, you can see an example of the definition of a work station (center), and in the next image, you can see an example of the sequence of these work centers along with its schedule details.
Therefore, when the production document related to the above product is created in the system and the production is terminated, the material consumption based on the BOM and the production operation cost based on the work centers and operating times are calculated by the system and included in the cost calculation. Note that the product pricing method can determine, for example, that the unit cost of each production batch is different from the other, or that it is distributed as an average and a value is displayed as the unit cost. The unit cost of each item can be seen on the card (identity card) of the corresponding product.
- Cost Accounting module in Business Central
In ERP Dynamics 365 Business Central, there is a dedicated module for industrial accounting, and you can operate the industrial accounting required in your organization in an environment separate from financial offices. In this module, you can create your desired cost structure in the organization based on the requirements of the collection. This module consists of the following elements:
- Classification of types of costs (Chart of Cost Types)
- Classification of types of cost centers (Chart of Cost Center)
- Classification of costs on the group of goods (Chart of Cost Objects)
- Allocation and sharing of costs (Cost Allocation)
In the Chart of Cost Type, the organization can create a tree of its costs based on its needs. This tree of expenses, which shows the different types of expenses of the organization, can be based on and similar to the chart of account of the general ledger or have minor or major differences with it. But it can still call the actual data from the chart of accounts based on the settings made and aggregate and display the expenses in a 1:1 or N:1 format. Direct costs in the unit cost can be applied from this point of identification.
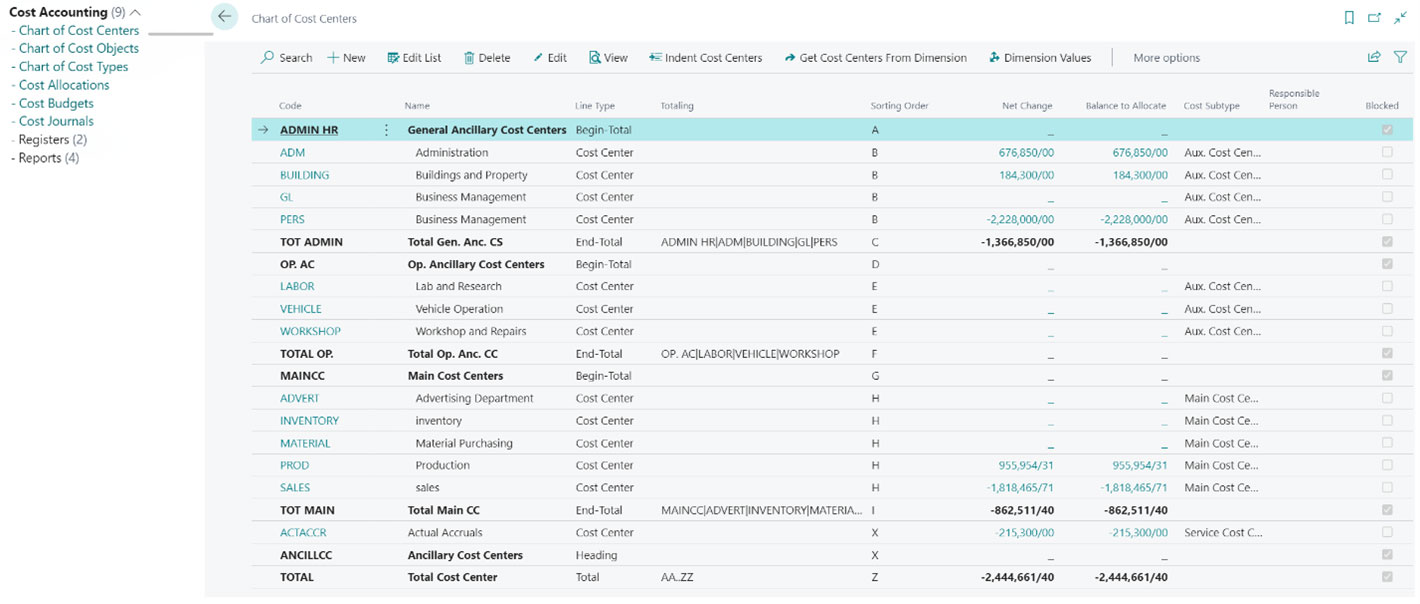
Chart of Cost Centers includes the definition of cost centers, where the costs of the organization are realized. Cost centers can be items such as production, administrative, sales, transportation, departmental, etc. costs. Indirect costs are identified from this section and affect the cost of goods. Finally, the Chart of Cost Object clearly determines the relevance and location of the cost from the point of view of the product or product group that is affected. The content and data of these two parts can be called through the dimensions defined in the financial part.
Finally, using Cost Allocation, you can statically or dynamically allocate costs according to the categories you want. For example, the fixed costs of the building can be statically calculated and applied dynamically. Also, if needed, it is possible to define correction rows and you can flexibly make your desired changes. In this way, all expenses will be at your disposal to calculate the unit cost and present it in the profit and loss statement of the company.
Cost Budget: Another option available to you in this section is budgeting for the organization’s expenses. Therefore, you can budget for your expense headings and finally compare the actual data with your budget and evaluate the amount of deviation.
Conclusion
Correct unit cost calculation is one of the important concerns of managers in many organizations. Despite the fact that the rules and regulations related to the unit cost and calculation formulas are simple, the existence of correct and structured data along with the existence of a suitable, specialized and standard platform to perform the desired operations in cost accounting are the important challenges of this matter. Also, despite the common generalities, this issue in every organization needs to be analyzed and implemented according to the specific needs of the business.
Dynamics 365 Business Central, as an integrated platform for all the main processes of the organization, can firstly solve the data problem in the organization, and secondly, by means of the facilities and standard elements that it provides to organizations in this field, it can calculate the unit cost accurately.